Discover what databases are using
encryption.

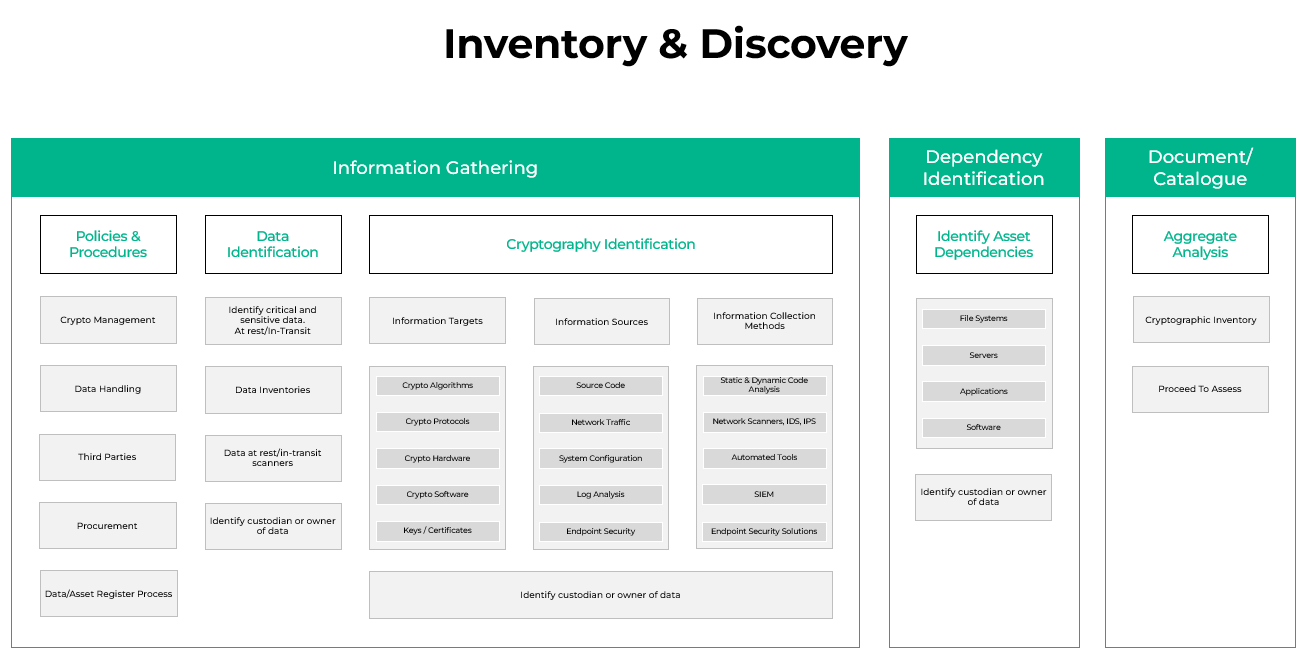
Step 1 for Post-Quantum Cryptography Transition is Inventory: The Five Pillars of Cryptographic Discovery & Inventory.
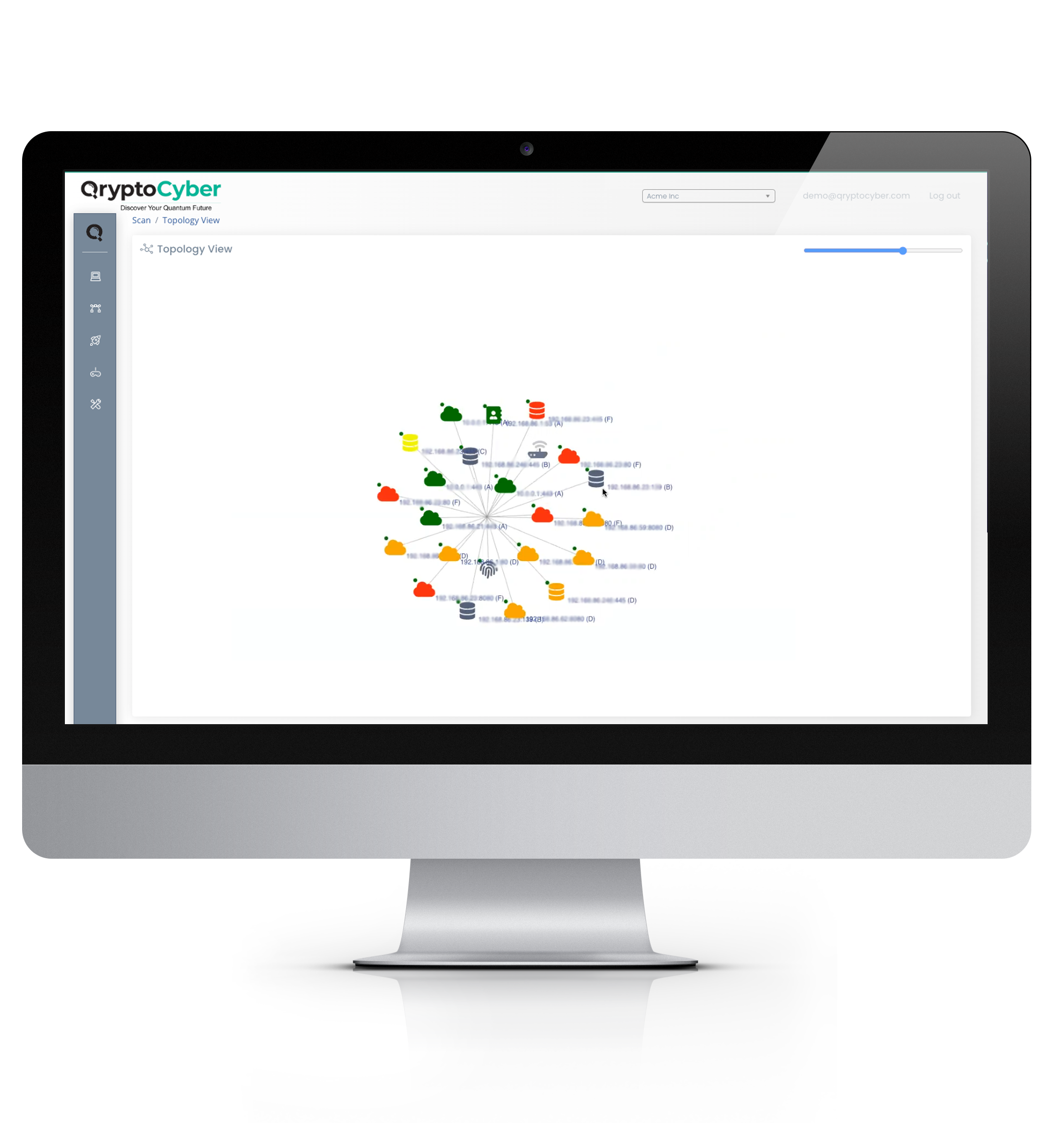
Database Encryption Scanning
Inventory Encryption Across All Databases
The fourth pillar focuses on the critical need to secure databases, a prime target for cyberattacks due to their storage of sensitive personal, financial, and intellectual property data.
A thorough cryptographic inventory of databases should assess current encryption practices, key management processes, and quantum-resilience standards to safeguard these assets effectively.
This inventory begins by identifying all databases, including relational types like MySQL and non-relational ones like MongoDB.
It’s essential to evaluate the encryption methods used, ensuring they are robust both at rest and in transit and flagging any outdated algorithms. Additionally, encryption key management must be reviewed to confirm that keys are securely stored and rotated regularly.
As quantum computing progresses, exploring quantum-safe encryption and key management solutions becomes a proactive measure in fortifying database security.
Databases
The fourth pillar emphasizes the importance of securing Databases. Databases are a prime target for cyberattacks, as they often contain sensitive personal data, financial information, and intellectual property. Export a machine‑readable CBOM that catalogs your database cryptographic inventory for risk assessment and compliance.
A cryptographic inventory must include a detailed analysis of how databases are encrypted, how encryption keys are managed, and whether quantum-safe encryption standards are applied.
Key steps in this pillar include:
Discover and inventory databases
Identify all databases within the organization, including relational databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL) and non-relational databases (e.g., MongoDB, Cassandra).
01
Evaluate encryption mechanisms
Ensure that databases are encrypted at rest and in transit using strong algorithms, and identify any databases that still rely on deprecated encryption standards.
02
Assess key management practices
Review the management of encryption keys to ensure they are stored securely and are regularly rotated. In preparation for quantum computing, organizations should explore quantum-safe key management solutions.
03
Identifying Critical and Sensitive Data:
Classifying data based on its sensitivity level helps organizations prioritize encryption efforts, applying stronger protection to high-risk information. This is particularly important for data at rest (stored in databases and other storage systems)
A proactive approach to encryption and data security in databases forms a vital component of any cryptographic risk management strategy.
Solution Architecture
External (either Software As A Service, Private Cloud, Customer Provided environment), internally hosted as a docker image or consultant managed. managed.
Relational
NoSQL
Cloud
Object
Time Series
Starting is the easiest part.
The problem won’t get easier with time. The first step is both the simplest and easiest. Put your foot on the path and start walking to the post quantum future.

