The Cryptographic Inventory Journey: CISA, NSA & NIST: Migration to Post Quantum Cryptography
Introduction
In today’s digital age, where data breaches and cyber threats are rampant, organizations must adopt robust security measures to protect sensitive information. One such critical measure is the implementation of a cryptographic inventory. As we stand on the brink of the quantum computing era, understanding and managing cryptographic assets becomes paramount. This blog will explore the concept of cryptographic inventory, its significance, and the steps organizations can take to ensure their security posture is quantum-ready.
What is Cryptographic Inventory?
Cryptographic inventory is a comprehensive and systematic documentation of all cryptographic assets within an organization. These assets include encryption algorithms, cryptographic keys, certificates, and other related elements. By maintaining a detailed inventory, organizations can gain visibility and control over their cryptographic landscape, ensuring that all assets are up-to-date, secure, and compliant with industry standards.
Importance of Cryptographic Inventory
- Enhanced Visibility and Control: A cryptographic inventory provides a clear and comprehensive view of all cryptographic assets, enabling organizations to manage and monitor them effectively. This visibility helps in identifying outdated or weak encryption methods that could pose security risks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Various regulatory bodies and industry standards require organizations to maintain a robust cryptographic framework. A well-maintained cryptographic inventory ensures compliance with these regulations, avoiding potential fines and reputational damage.
- Risk Management: By regularly updating and reviewing cryptographic assets, organizations can identify and mitigate risks associated with obsolete or vulnerable encryption methods. This proactive approach helps in safeguarding sensitive data from potential breaches.
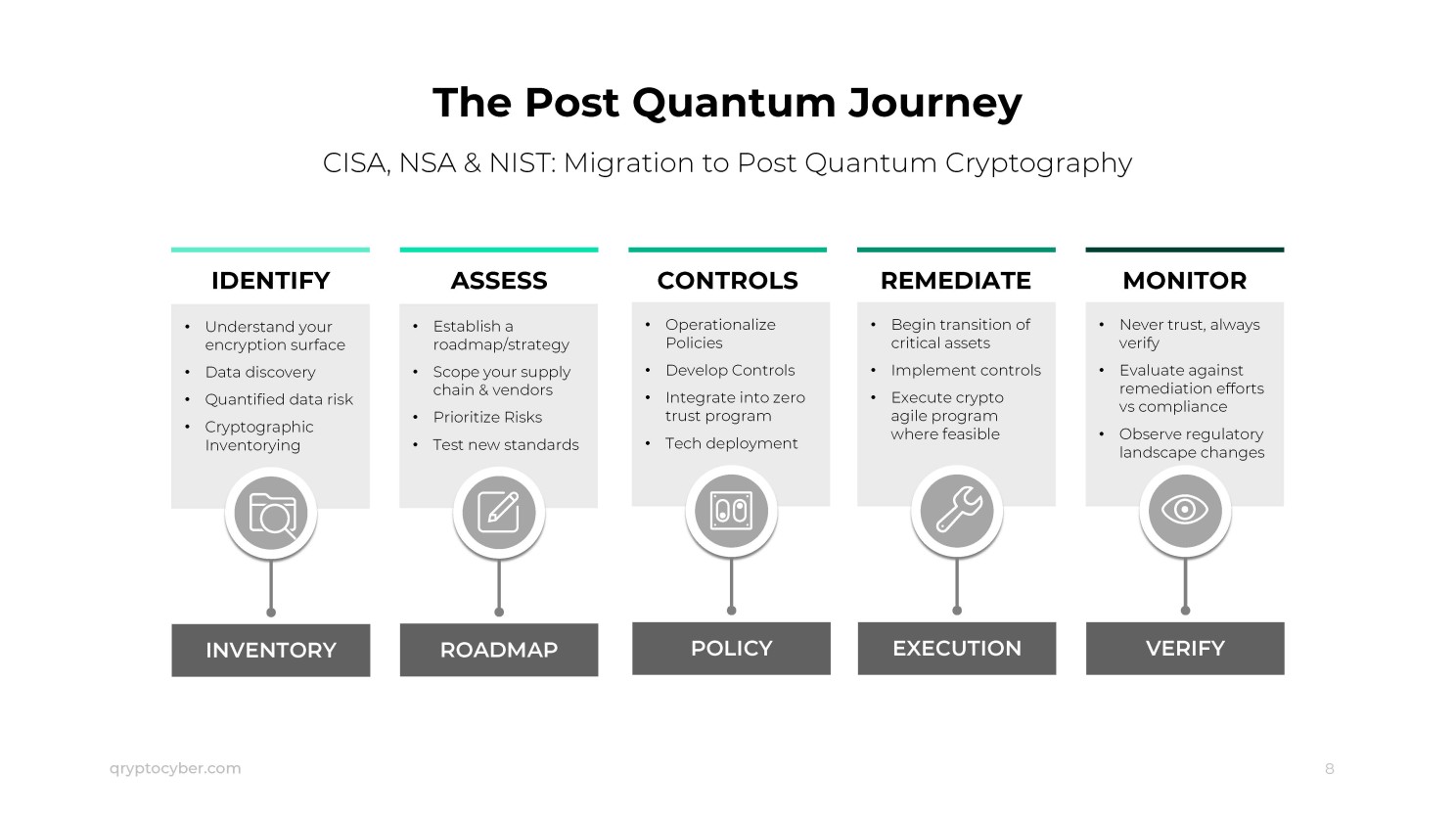
Steps to Implement a Cryptographic Inventory
- Asset Identification: The first step in creating a cryptographic inventory is identifying all cryptographic assets within the organization. This includes encryption algorithms, cryptographic keys, certificates, and any other relevant components.
- Assessment and Evaluation: Once all assets are identified, they need to be assessed for their strength, relevance, and compliance with current security standards. This evaluation helps in identifying assets that need to be updated or replaced.
- Documentation: Detailed records of all cryptographic assets should be maintained, including their usage, expiry dates, and any changes made. This documentation ensures that all assets are tracked and managed effectively.
- Continuous Monitoring and Updates: A cryptographic inventory is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. Regular monitoring and updates are essential to ensure that all assets remain secure and compliant with evolving security standards.
Conclusion
In the face of advancing quantum computing capabilities, maintaining a robust cryptographic inventory is not just a best practice but a necessity. By implementing a systematic approach to managing cryptographic assets, organizations can ensure their security posture is strong and resilient. This proactive measure will not only protect sensitive data but also prepare organizations for the quantum era, where traditional encryption methods may no longer suffice.