Cryptographic Discovery & Inventory for Quantum Risk: Preparing for the Quantum Future
As quantum computing progresses from theoretical research to practical applications, its impact on cybersecurity becomes increasingly significant. The cryptographic methods that secure our data today, such as RSA and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), are at risk of becoming obsolete in the face of quantum algorithms capable of breaking them. To mitigate this looming threat, organizations must adopt a proactive approach through Cryptographic Discovery & Inventory for Quantum Risk.
Understanding the Quantum Threat
Quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations at unprecedented speeds. While this holds immense promise for fields like drug discovery and material science, it poses a severe threat to cybersecurity. Quantum computers can potentially break widely-used cryptographic algorithms, such as RSA, which relies on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers—a task that quantum computers can accomplish exponentially faster.
The Need for Cryptographic Discovery
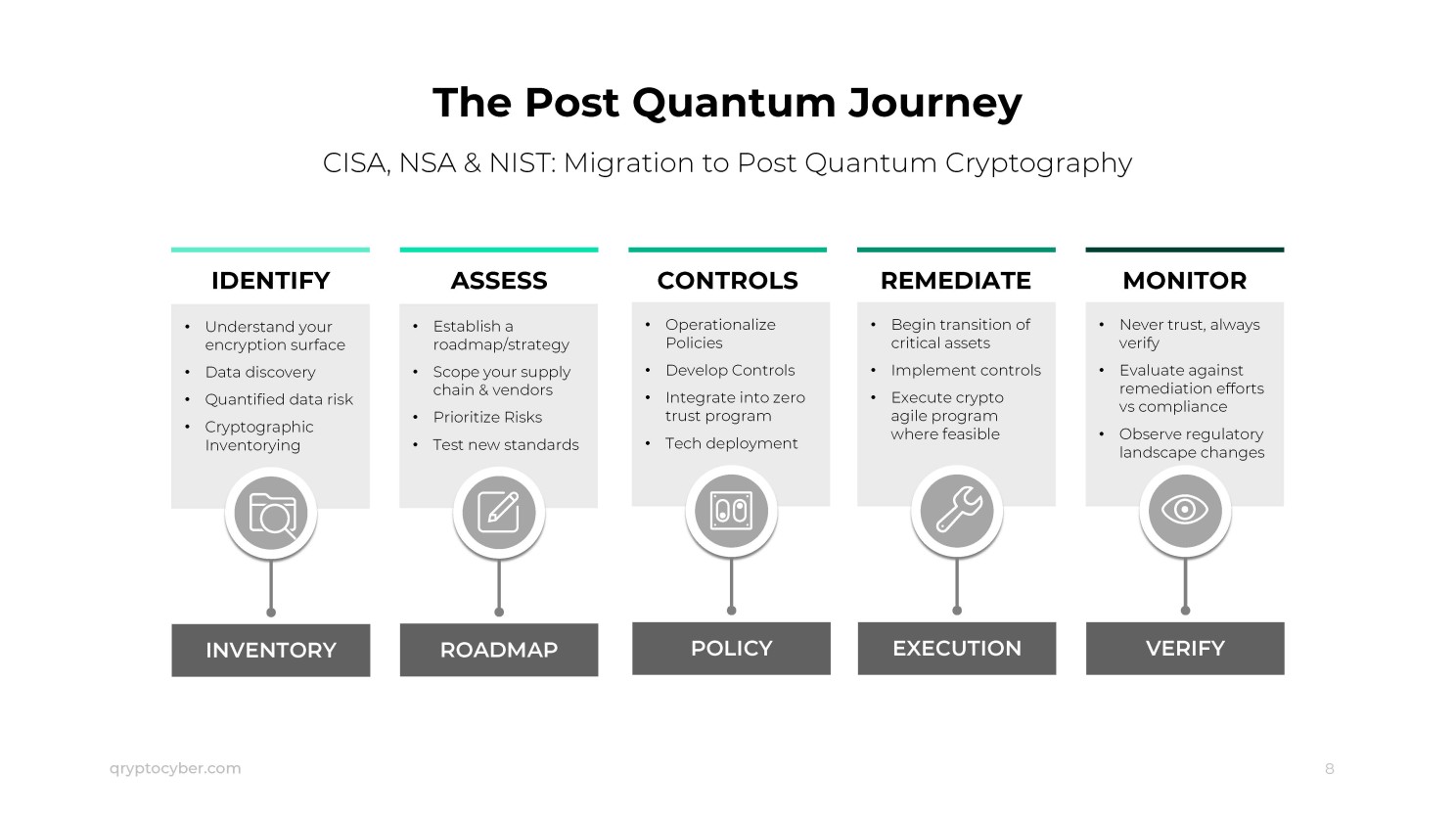
The first step in addressing quantum risk is identifying all cryptographic assets within an organization. Cryptographic Discovery involves a thorough examination of systems, applications, and data flows to locate and document every instance of encryption. This includes:
- Encryption keys: Identifying all encryption keys used across the organization.
- Algorithms: Cataloging the cryptographic algorithms in use.
- Protocols: Documenting the communication protocols that rely on cryptographic methods.
- Certificates: Identifying digital certificates and their dependencies.
A comprehensive understanding of these assets is crucial to assess their vulnerability to quantum attacks and prioritize the transition to quantum-resistant alternatives.
Building the Cryptographic Inventory
Once the discovery phase is complete, organizations must build a detailed inventory of their cryptographic assets. This inventory serves as a centralized repository for tracking and managing cryptographic resources. Key elements of a robust cryptographic inventory include:
- Asset Classification: Categorizing cryptographic assets based on their sensitivity and criticality.
- Lifecycle Management: Tracking the lifecycle of cryptographic assets, from creation and deployment to retirement.
- Usage Mapping: Mapping the usage of cryptographic assets across various systems and applications.
- Compliance Tracking: Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
A well-maintained cryptographic inventory enables organizations to monitor the status of their cryptographic assets continuously, identify outdated or vulnerable components, and plan for timely upgrades or replacements.
Transitioning to Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
With a clear understanding of their cryptographic landscape, organizations can begin transitioning to quantum-resistant cryptographic solutions. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is leading the effort to standardize post-quantum cryptographic algorithms. Organizations should stay informed about these developments and plan to adopt these new standards once they are finalized.
Practical Steps for Quantum Readiness
- Education and Awareness: Educate stakeholders about the quantum threat and the importance of cryptographic readiness.
- Policy Development: Develop policies and guidelines for managing cryptographic assets in the context of quantum risk.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a risk assessment to identify the most critical cryptographic assets and prioritize their transition to quantum-resistant alternatives.
- Pilot Testing: Implement pilot projects to test and validate quantum-resistant algorithms and solutions.
- Vendor Collaboration: Collaborate with vendors and partners to ensure their products and services are aligned with quantum readiness goals.
Conclusion
The transition to a quantum-secure future is a complex but necessary journey. Cryptographic Discovery & Inventory for Quantum Risk is a foundational step in this process, enabling organizations to understand their cryptographic landscape, manage assets effectively, and transition to quantum-resistant solutions. By taking proactive measures today, organizations can safeguard their data and maintain trust in their security practices as quantum computing becomes a reality. Preparing for quantum risk is not just a technical necessity but a strategic imperative for the future of cybersecurity.